本文目的:通过React构建一个可搜索的产品数据表格,来更深刻地领会React哲学。
1、从设计稿开始
-
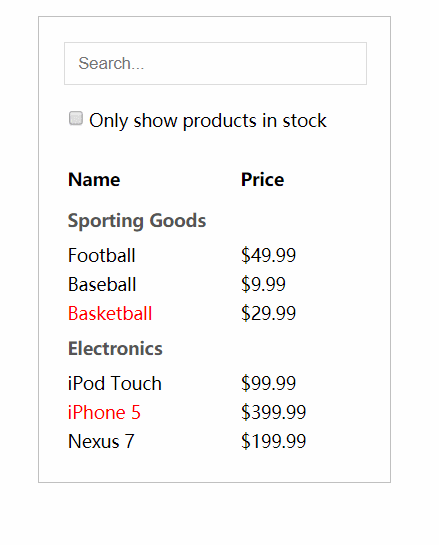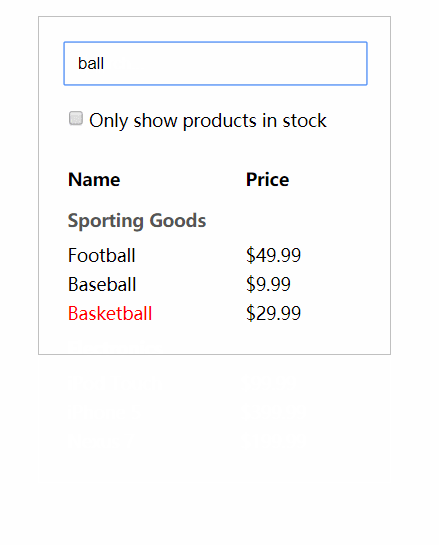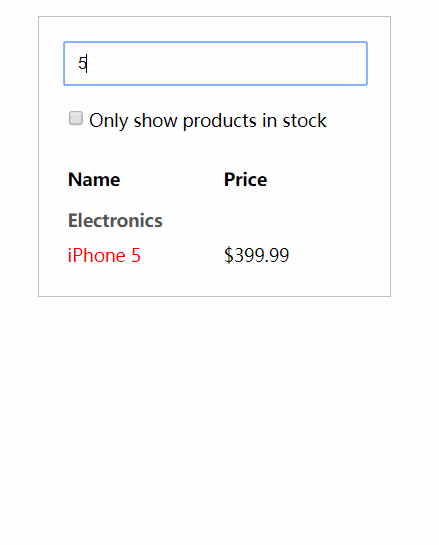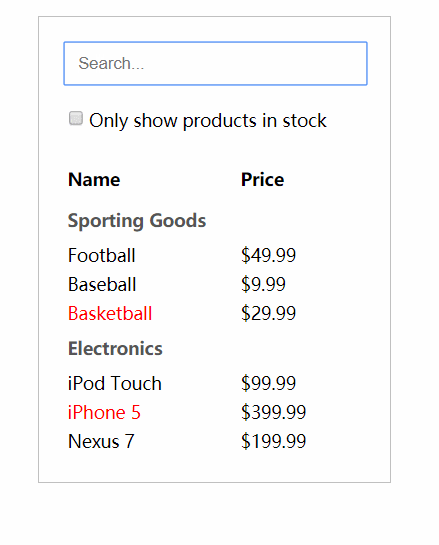
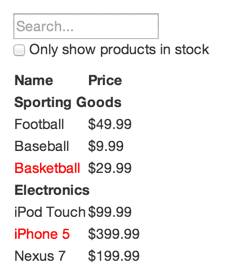
效果图:
- JSON API返回以下数据:
12345678[{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$49.99", stocked: true, name: "Football"},{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$9.99", stocked: true, name: "Baseball"},{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$29.99", stocked: false, name: "Basketball"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$99.99", stocked: true, name: "iPod Touch"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$399.99", stocked: false, name: "iPhone 5"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$199.99", stocked: true, name: "Nexus 7"}];
2、第一步:将设计好的 UI 划分为组件层级
- 首先,在设计稿上圈出每个组件(以及组件的子组件),并以合适的名称命名。
- 如何确定将哪些组件划分到一个组件中?
- 可以将组件当作一种函数或者对象来考虑,根据单一功能原则来判定组件的范围。
- 一个组件原则上只能负责一个功能。
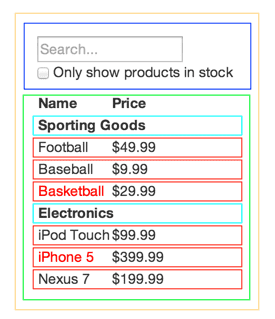
- 上图包含五个组件:
- 1.橙色(FilterableProductTable):整个示例应用的整体
- 2.蓝色(SearchBar):用户输入
- 3.绿色(ProductTable):数据内容
- 4.天蓝色(ProductCategoryRow):产品类别
- 5.红色(ProductRow):产品
- 更加清晰的层级【设计稿中被其他组件包含的子组件,在层级上应该作为其子节点】
- FilterableProductTable
- SearchBar
- ProductTable
- ProductCategoryRow
- ProductRow
- FilterableProductTable
3、第二步:用 React 创建一个静态版本
-
先用已有的数据模型,渲染一个不包含交互功能的UI
-
自上而下或者自下而上构建应用
- 自上而下
- 先编写层级较高的组件
- 适用于比较简单的应用
- 自下而上
- 从最基本的组件开始编写
- 便于大型项目为低层组件编写测试
- 自上而下
-
代码:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990919293949596979899100101102103104105106107108109110111<script type="text/babel">// 5.产品class ProductRow extends React.Component {render () {const product = this.props.productconst name = product.stocked ?product.name :<span style={{ color: 'red' }}>{ product.name }</span>return (<tr class="product-row"><td>{ name }</td><td>{ product.price }</td></tr>)}}// 4.产品类别class ProductCategoryRow extends React.Component {render () {const category = this.props.categoryreturn (<tr class="product-category-row"><th colspan="2">{ category }</th></tr>)}}// 3.数据内容class ProductTable extends React.Component {render () {const rows = []let lastCategory = nullthis.props.products.forEach((product) => {if (product.category !== lastCategory) {rows.push(<ProductCategoryRowkey={ product.category }category={ product.category } />)}rows.push(<ProductRowproduct={ product }key={ product.name } />)lastCategory = product.category})return (<table class="product-table"><thead><tr><th>Name</th><th>Price</th></tr></thead><tbody>{ rows }</tbody></table>)}}// 2.用户输入class SearchBar extends React.Component {render () {return (<form class="search-bar"><input type="text" placeholder="Search..." class="keyword" /><p><input type="checkbox" />{''}Only show products in stock</p></form>)}}// 1.示例整体class FilterableProductTable extends React.Component {render () {return (<div class="filterable-product-table"><SearchBar /><ProductTable products={ this.props.products } /></div>)}}// JSON APIconst PRODUCTS = [{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$49.99", stocked: true, name: "Football"},{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$9.99", stocked: true, name: "Baseball"},{category: "Sporting Goods", price: "$29.99", stocked: false, name: "Basketball"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$99.99", stocked: true, name: "iPod Touch"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$399.99", stocked: false, name: "iPhone 5"},{category: "Electronics", price: "$199.99", stocked: true, name: "Nexus 7"}]ReactDOM.render(<FilterableProductTable products={ PRODUCTS } />,document.getElementById('root'))</script>123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930<style>.filterable-product-table {width: 240px;border: 1px solid silver;padding: 20px;margin: 100px;font-size: 14px;}.search-bar {line-height: 30px;}.search-bar .keyword {width: 100%;height: 30px;border: 1px solid #ddd;text-indent: 10px;}.product-table {margin-top: 15px;width: 100%;text-align: left;line-height: 30px;}.product-category-row {color: #555;}.product-row {line-height: 20px;}</style> -
React 单向数据流(也叫单向绑定)的思想使得组件模块化,易于快速开发。
4、第三步:确定UI state的最小(且完整)表示
- 目的:找出应用所需的state的最小表示,并根据需要计算出其他所有数据
- 关键:DRY【Don’t Repeat Yourself】
- 如何检查数据是否属于state?
- 该数据是否是由父组件通过 props 传递而来的?如果是,那它应该不是 state。
- 该数据是否随时间的推移而保持不变?如果是,那它应该也不是 state。
- 你能否根据其他 state 或 props 计算出该数据的值?如果是,那它也不是 state。
- 示例应用数据分析:
- 1.包含所有产品的原始列表
- 不是state:包含所有产品的原始列表是经由 props 传入的
- 2.搜索关键词
- 是state:随时间会发生改变且无法由其他数据计算而来
- 3.复选框是否选中的值
- 是state:随时间会发生改变且无法由其他数据计算而来
- 4.搜索筛选的产品列表
- 不是state:结果可以由产品的原始列表根据搜索词和复选框的选择计算出来
- 1.包含所有产品的原始列表
5、第四步:确定state放置的位置
注意:React 中的数据流是单向的,并顺着组件层级从上往下传递。
- 判断state应该放在哪个组件中?
- 找到根据这个 state 进行渲染的所有组件。
- 找到他们的共同所有者(common owner)组件(在组件层级上高于所有需要该 state 的组件)。
- 该共同所有者组件或者比它层级更高的组件应该拥有该 state。
- 如果你找不到一个合适的位置来存放该 state,就可以直接创建一个新的组件来存放该 state,并将这一新组件置于高于共同所有者组件层级的位置。
- 分析示例应用:
ProductTable需要根据 state 筛选产品列表。SearchBar需要展示搜索词和复选框的状态。- 他们的共同所有者是
FilterableProductTable。 - 因此,搜索词和复选框的值应该很自然地存放在
FilterableProductTable组件中。
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 |
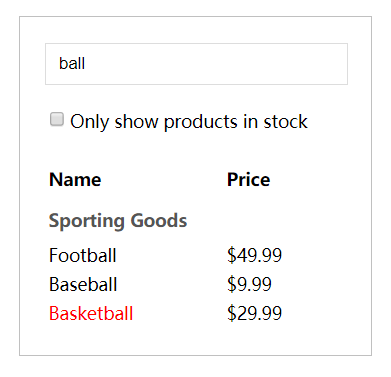
// step4 // 3.数据内容 class ProductTable2 extends React.Component { render () { const filterText = this.props.filterText const inStockOnly = this.props.inStockOnly const rows = [] let lastCategory = null this.props.products.forEach((product) => { if (product.name.indexOf(filterText) === -1) { return } if (inStockOnly && !prodcut.stocked) { return } if (product.category !== lastCategory) { rows.push( <ProductCategoryRow key={ product.category } category={ product.category } /> ) } rows.push( <ProductRow product={ product } key={ product.name } /> ) lastCategory = product.category }) return ( <table class="product-table"> <thead> <tr> <th>Name</th> <th>Price</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody>{ rows }</tbody> </table> ) } } // 2.用户输入 class SearchBar2 extends React.Component { render () { const filterText = this.props.filterText const inStockOnly = this.props.inStockOnly return ( <form class="search-bar"> <input type="text" placeholder="Search..." class="keyword" value={ filterText } /> <p> <input type="checkbox" checked={ inStockOnly } /> {''} Only show products in stock </p> </form> ) } } // 1.示例整体 class FilterableProductTable2 extends React.Component { constructor (props) { super(props) this.state = { filterText: 'ball', inStockOnly: false } } render () { return ( <div class="filterable-product-table"> <SearchBar2 filterText={ this.state.filterText } inStockOnly={ this.state.inStockOnly } /> <ProductTable2 products={ this.props.products } filterText={ this.state.filterText } inStockOnly={ this.state.inStockOnly } /> </div> ) } } ReactDOM.render( <FilterableProductTable2 products={ PRODUCTS } />, document.getElementById('root2') ) |
6、第五步:添加反向数据流
-
React 通过一种比传统的双向绑定略微繁琐的方法来实现反向数据传递。
-
代码:
123456789101112131415161718192021222324252627282930313233343536373839404142434445464748495051525354555657585960616263646566676869707172737475767778798081828384858687888990// step5// 2.用户输入class SearchBar3 extends React.Component {constructor (props) {super(props)this.handleFilterTextChange = this.handleFilterTextChange.bind(this)this.handleInStockChange = this.handleInStockChange.bind(this)}handleFilterTextChange (e) {this.props.onFilterTextChange(e.target.value)}handleInStockChange (e) {this.props.onInStockChange(e.target.checked)}render () {const filterText = this.props.filterTextconst inStockOnly = this.props.inStockOnlyreturn (<form class="search-bar"><inputtype="text"placeholder="Search..."class="keyword"value={ filterText }onChange={ this.handleFilterTextChange } /><p><inputtype="checkbox"checked={ inStockOnly }onChange={ this.handleInStockChange } />{''}Only show products in stock</p></form>)}}// 1.示例整体class FilterableProductTable3 extends React.Component {constructor (props) {super(props)this.state = {filterText: '',inStockOnly: false}this.handleFilterTextChange = this.handleFilterTextChange.bind(this)this.handleInStockChange = this.handleInStockChange.bind(this)}handleFilterTextChange (filterText) {this.setState({filterText: filterText})}handleInStockChange (inStockOnly) {this.setState({inStockOnly: inStockOnly})}render () {return (<div class="filterable-product-table"><SearchBar3filterText={ this.state.filterText }inStockOnly={ this.state.inStockOnly }onFilterTextChange={ this.handleFilterTextChange }onInStockChange={ this.handleInStockChange } /><ProductTable2products={ this.props.products }filterText={ this.state.filterText }inStockOnly={ this.state.inStockOnly } /></div>)}}ReactDOM.render(<FilterableProductTable3 products={ PRODUCTS } />,document.getElementById('root3'))